Air sampling is known as capturing the
contaminant from a known volume of air, measuring the amount of contaminant
captured, and expressing it as a concentration. It often is associated with the
industrial work place or places where chemicals are used often or produced.
Sampling air is conducted by using devices that measure and evaluate a sample,
or multiple samples or the air. Some of the most dangerous hazards that pollute
that air are man-made chemical compounds such as gases and vapors.
It is so important to conduct regular air
samples because these potential hazards could harm any person or employee that
spends time is said environment. These damages could be immediate or long term.
Higher levels of contaminants such as toxic gases can cause direct and
sometimes fatal outcomes. Contaminants at lower levels still have a major
impact but result in illness and disease that gradually builds up in the body
over time. It is imperative that air sampling is conducted regularly even if
there are no obvious threats present. Keeping up with air sampling is apart of
occupational health and safety standards.
Pump calibration is a way of sampling air
in the field. The first step in to assemble the pump by connected the
calibrated personal pump with plastic tubing to the collection media. The piece
is attached with a holder that clips on and allows it to be attached to
someone’s collar in the breathing zone.
Breathing zone sampling is personal
because it only measures and evaluates that individual’s exposure to chemicals.
They are called breathing zones because it is measured by an individual’s nose
and mouth area. This method is the best way to accurately quantify the exact
concentration of contaminants in the air that the person is actually breathing
and taking into their body.
NIOSH method number 2027 is a sampling and analytical method for 6 ketone compounds in workplace air. The volume of air is calculated by multiplying the flow rate through the filter medium by the time in minutes. Calibration of the flow rate is important and should be carried out before and after each sample is taken.
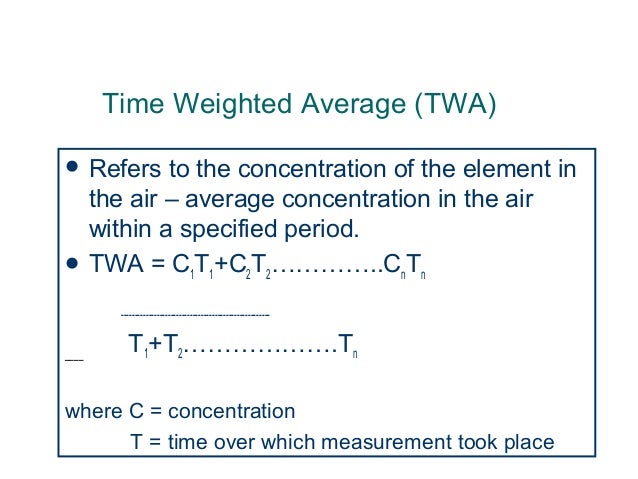
There are multiple ways to measure air samples, but the most common is a battery operated pump. This machine is capable of collecting air through a filter at a constant rate over a period of eight hours. This can take place no matter what type of weather persists. These recommendations are to take a personal basis for an eight hour Time Weighted Average.
Industrial and construction sites are a very high risk for dangerous exposure. All the procedures are necessary to ensure a safe workplace. Without it, the staff may be prone to coming encounter with harmful dust, vapours, or gases. The most noteworthy route of entry is through inhalation into the body. It is vital to stay on top of these regulations to know that employees and other people will remain safe from harmful chemicals. Air sampling protects workers and the environment, but also the practice of taking samples of air can be helpful in determining what kind of protective clothing should be selected for worker safety.